Sunday, December 30, 2012
Raspberry Pi 13 Port USB Hub
I bought one today which is not exactly mentioned over at the Raspberry Pi peripheral compatibility list (powered USB hub section). However, once I used the hub, I checked the USB device id with lsusb. It turns out the device id is in there: 1A40:0201 which translates to Terminus Technology Inc. FE 2.1 7-port Hub. The hub itself named Mumuksu (product code: MU109) and contains 13 USB ports. The cost is around $17. It comes with a power adapter (US-type connector unfortunately, so I needed a converter coz in my country the plug is European type). The power adapter output is rated at 5V and 3A.
The USB hub is powerful enough to power USB HDD and "back-power-ing" the Raspberry Pi without problem. I have yet to add another power hungry device to the mix. But again, this shows that one of the indicator of a good USB hub for raspberry pi is the huge amount of current that it provides.
Friday, December 28, 2012
Raspberry Pi LXDE (X Server) Auto Login
All is great with that, but I'm curious to know what exactly the raspi-config script do to accomplish that. Well, time to fire up grep and do some digging. I found several remnants left by raspi-config while executing this command:
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ sudo grep -r -w 'pi' /etc/ | lessThere is an intriguing result while scrolling through less output like these:
... /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf:autologin-user=pi ... /etc/passwd:pi:x:1000:1000:,,,:/home/pi:/bin/bash /etc/passwd-:pi:x:1000:1000:,,,:/home/pi:/bin/bashI have yet to decipher the whole stuff, but searching for the remnants of the intriguing raspi-config changes is certainly worthwile.
Thursday, December 27, 2012
Calling Python Module from C
/** \brief This function executes python module passed in args[0]
*
* \param argCount number of arguments passed to this function in args parameter
* \param args array of string containing the parameters. The first parameter is
* the name of the python module, the second parameter is the
* function name in the python module. The third and latter parameters
* are the parameters to the python function in the python module.
*/
int
exec_python_module(int argCount, char *args[])
{
PyObject *pName, *pModule, *pDict, *pFunc;
PyObject *pArgs, *pValue, *pFloatValue;
int i;
if (argCount < 2) {
fprintf(stderr,"exec_python_module() usage: pythonfile funcname [args]\n");
return 1;
}
Py_Initialize();
pName = PyString_FromString(args[0]);
/* Error checking of pName left out */
pModule = PyImport_Import(pName);
Py_DECREF(pName);
if (pModule != NULL) {
pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, args[1]);
/* pFunc is a new reference */
if (pFunc && PyCallable_Check(pFunc)) {
/* NOTE: The function parameters start at
args[2], that's why the index must be
subtracted with two below */
pArgs = PyTuple_New(argCount - 2);
for (i = 0; i < argCount - 2; ++i) {
pValue = PyString_FromString(args[i + 2]);
if (!pValue) {
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot convert argument\n");
return 1;
}
/* pValue reference stolen here: */
PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, i, pValue);
}
pValue = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, pArgs);
Py_DECREF(pArgs);
if (pValue != NULL) {
printf("Result of call: %ld\n", PyInt_AsLong(pValue));
Py_DECREF(pValue);
}
else {
Py_DECREF(pFunc);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr,"Call failed\n");
return 1;
}
}
else {
if (PyErr_Occurred())
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot find function \"%s\"\n", args[1]);
}
Py_XDECREF(pFunc);
Py_DECREF(pModule);
}
else {
PyErr_Print();
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to load \"%s\" module\n", args[0]);
return 1;
}
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}
The main difference to the sample code in python 2.7.3 docs (section Embedding Python in Another Application | Pure Embedding) is that instead of PyInt_FromLong(), I'm using PyString_FromString() function. Therefore, the assumption is that all of the function arguments are passed as string, in order not to truncate anything.It's the job of the python function to convert to the right type as needed. For example, if you pass float value as string then you have to convert the float string to float in your python code. Let's see how to do this. Take a look at the python function as follows:
def My_Function(my_float_string_param):
converted_float = float(my_float_string_param)
## Process using float here
## ...
The python code above converts the float string into float with the float() function. This is needed, otherwise the python interpreter would balk out with error message if you use my_float_string_param directly on function calls that expects a python float variable. Instead of using my_float_string_param, you should use converted_float in those function calls.
Adding New Path to PYTHONPATH
me@mymachine ~/work $ python Python 2.7.3rc2 (default, May 6 2012, 20:02:25) [GCC 4.6.3] on linux2 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> import sys >>> sys.path ['', '/usr/lib/python2.7', '/usr/lib/python2.7/plat-linux2', '/usr/lib/python2.7/lib-tk', '/usr/lib/python2.7/lib-old', '/usr/lib/python2.7/lib-dynload', '/usr/local/lib/python2.7/dist-packages', '/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages', '/home/pi/work/c_to_python', '/usr/lib/pymodules/python2.7'] >>>This link explains the alternatives to do that. I choose the easiest path, i.e. adding a *.pth file to one of the path already parsed by python. For example, adding my_path.pth to /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages directory, with the content of my_path.pth as follows:
/home/me/my_python_lib_dirThis of course assume that your python module is in /home/me/my_python_lib_dir. That's it, hopefully this could be useful for those wanting to place a python module in "non-standard" python path(s).
Wednesday, December 26, 2012
Moving Raspberry Pi Root Filesystem Out of SDcard
Now, I'll show you how to move the / partition to a USB flash drive. First, copy the contents of your present / in the SDcard to the USB flash drive with dd, I assume that the USB flash drive is recognized as /dev/sda1 by the Raspberry Pi kernel. Anyway, ordinary cp command wouldn't work because it doesn't copy the partition structure.
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ dd if=/dev/mmcblk0p2 of=/dev/sda1 bs=512Now, get yourself some coffee and work on something else or go to sleep because this would take hours if you have enlarged your SDcard / partition to say 8GB.
The second step is to change the parameters passed to the raspberry pi kernel on boot. The purpose is to change the / (root) partition from mmcblk0p2 to sda1. To do that, you have to edit /boot/cmdline.txt. You can do this step from windows because cmdline.txt is in the vfat partition in the beginning of the SDcard. This is how the parameters passed to the kernel look like after the change (I highlighted the change in italic):
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0 console=ttyAMA0,115200 kgdboc=ttyAMA0,115200 console=tty1 root=/dev/sda1 rootfstype=ext4 elevator=deadline rootwaitThis is not enough though, you have to change /etc/fstab in the Raspberry Pi (USB flash drive) once the system booted. Remember that you have to plug the USB flash drive after you changed the kernel boot parameter! Because raspberry pi kernel would think that the / (root filesystem) is now in /dev/sda1. This is how the modified /etc/fstab looks like:
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0 /dev/mmcblk0p1 /boot vfat defaults,ro 0 2 #/dev/mmcblk0p2 / ext4 defaults,noatime 0 1 /dev/sda1 / ext4 defaults,noatime 0 1 # a swapfile is not a swap partition, so no using swapon|off from here on, use dphys-swapfile swap[on|off] for thatAs you can see, I have commented the /dev/mmcblk0p2 root filesystem which corresponds to the second partition in the SDcard. After this change, you can reboot the system and be sure that the / will not be on the SDCard anymore.
Anyway, if you pay attention to the /etc/fstab entries above, you would notice that I mounted /boot in read-only mode. This is to prevent the kernel from writing into the SDcard. In a deployment scenario, it's better to make the entire SDcard mounted in read-only mode, unless you have very specific need to write into one of the SDcard partition.
Friday, December 21, 2012
Embedding Python Code in C - The Raspberry Pi Edition
Let's put the lesson in those source to good use. The target is Raspberry Pi with Debian "Wheezy".
First up, install python-dev package to your Raspberry Pi. This will also install all required packages if they're not yet installed.
sudo apt-get install python-devWe need the python-dev package to obtain python-config, the C header files and libraries to link out C code with the python interpreter.
After python-dev installed. We need to find what are the GCC linker parameters that we need to use to link to the python interpreter in Raspberry Pi. In many cases this will be different from the linker parameters in your desktop (x86) distro. This is the command to know the GCC linker parameters:
pi@raspberrypi ~/experiments/c_to_python $ python-config --ldflags -L/usr/lib/python2.7/config -lpthread -ldl -lutil -lm -lpython2.7 -Xlinker -export-dynamic -Wl,-O1 -Wl,-Bsymbolic-functionsAs you can see, it's pretty long. We're going to need it in our Makefile later.
Now, let's make a very simple C program that invoke the python interpreter and print "hello" to the console from inside the interpreter. This is my code that has been tested and worked:
#include < python2.7/Python.h >
#include < stdio.h >
void exec_pycode(const char* py_code);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
exec_pycode("print \"hello\"");
return 0;
}
void exec_pycode(const char* py_code)
{
Py_Initialize();
PyRun_SimpleString(py_code);
Py_Finalize();
}
As you can see, the code is very simple. You will need to use a Makefile to build the application because the linker parameter is quite tedious to input by hand. This is how my Makefile looks like:
# compile c_to_python.c
default:
gcc -L/usr/lib/python2.7/config -lpthread -ldl -lutil -lm -lpython2.7 -Xlinker -export-dynamic -Wl,-O1 -Wl,-Bsymbolic-functions -o invoke_python c_to_python.c
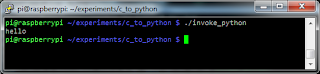
The C code in the preceding listing is in the file named c_to_python.c and the output file is named invoke_python. This is the result of the execution:It's not that hard, isn't it? From this point on, you can experiment with C programs that invokes python code. I have yet to find how to do this in a cross-compilation environment. For now, I have to do all the stuff in my Raspberry Pi (via ssh).
Thursday, December 20, 2012
Raspberry Pi Related Datasheets and Deep Look into Very Early Boot Stage
Thanks to the work of the FreeBSD guys, over at http://kernelnomicon.org/?m=201205, it get's much easier for me.
At this point, it's starting to look very similar to other embedded systems. I used to work on Realtek RTL8186 firmware and the stage to produce a working firmware is through a custom tool to "bind" all of the binaries into bootable binary. Have a look at Raspberry Pi mkimage tool over athttps://github.com/raspberrypi/tools/tree/master/mkimage. The python code in there (https://github.com/raspberrypi/tools/blob/master/mkimage/imagetool-uncompressed.py), really enlighten me how they're all put together into a working bootloader + kernel.
Tuesday, December 18, 2012
Headless PiLFS on Raspberry Pi
This is the static IP address once PiLFS finished booting: 192.168.2.2
The SSH user is (only one): root
with password: pilfs
I tried to sweep the whole 192.168.x.x IP address back then when I still didn't have (DVI) display to find where PiLFS might configure the system's ethernet, but failed to find any. Hopefully this helps those wanting to try Raspberry Pi with barebone DIY distro and having no access to display for his/her new Raspberry Pi.
Communicating from Raspberry Pi to ASP .NET MVC 4 Application
Now, let me start with the application running on Raspberry Pi. This is a very simple http client application that make use of the httplib library in python. It uses HTTP GET to read value from the ASP MVC4 WebApp application. This is the code:
import httplib
conn = httplib.HTTPConnection("192.168.137.1:8080")
conn.request("GET","/api/values/5")
r1 = conn.getresponse()
print r1.status, r1.reason
print r1.read()
As you can see, this application reads the value returned by the ASP MVC4 WebApp application at address http://192.168.137.1:8080/api/values/5. Before I continue explaining the ASP MVC4 portion, let's see the output of this application first when you run it and it gets response from the ASP MVC4 application:As you can see, the ASP MVC4 application returned the string "value" to the application in the Raspberry Pi.
Now let's move to the ASP MVC 4 application portion. The application is a default application generated when you choose to make WebApp-style application in ASP MVC 4. To do so, create a new project in Visual Studio 2010 or 2012 (I'm using Visual Studio 2010), select Visual C# | Web | ASP .NET MVC 4 Web Application then select Web API. Once your application source code is generated, everything on the server side is actually finished. What's left is configuration to make the ASP application accessible to Raspberry Pi.
There are three steps to make the application accessible through an ethernet connection to the Raspberry Pi.
- Configure your application to use IIS Express.
- Change IIS Express configuration for your application to "bind" it to the ethernet interface that's connected to Raspberry Pi.
- Enable access to your Raspberry Pi through Windows 7 firewall.
The second step is quite complicated. You need to modify your current windows login account setting for IIS Express. The file is located in C:\Users\[YourLoginName]\Documents\IISExpress\config\applicationhost.config (assuming your Windows 7 user accounts data is in C:\). In the applicationhost.config, go to your application settings in the element(s) inside <site>. In my case this is how it looks like before I made changes:
<site name="MvcApplication1" id="2">
<application path="/" applicationPool="Clr4IntegratedAppPool">
<virtualDirectory path="/" physicalPath="D:\Experiments\WCF\MvcApplication1\MvcApplication1" />
</application>
<bindings>
<binding protocol="http" bindingInformation="*:2086:localhost" />
</bindings>
</site>
Now, to make it IIS Express listens on certain network interface, we need to specifically tell it about the binding. This is accomplished by adding new binding in the binding protocol section. This is what I added to that section:
<binding protocol="http" bindingInformation="*:8080:192.168.137.1" />This binds IIS Express to the network interface with IP address 192.168.137.1 at port 8080. The application (MvcApplication1) setting now turns into:
<site name="MvcApplication1" id="2">
<application path="/" applicationPool="Clr4IntegratedAppPool">
<virtualDirectory path="/" physicalPath="D:\Experiments\WCF\MvcApplication1\MvcApplication1" />
</application>
<bindings>
<binding protocol="http" bindingInformation="*:2086:localhost" />
<binding protocol="http" bindingInformation="*:8080:192.168.137.1" />
</bindings>
</site>
Notice the change that happened in the binding protocol section. You can see similar explanation in this link: http://johan.driessen.se/posts/Accessing-an-IIS-Express-site-from-a-remote-computer.To test whether your IIS Express binding is working, run your application and use your browser to access the page from the ASP MVC4 application. For example, in my case, I use http://192.168.137.1:8080 to see wheter the binding works before I tried to connect from the python application in Raspberry Pi.
The last change to make is to tell the Firewall to accept access from the Raspberry Pi. In my case I made a custom rule in the Firewall (through the firewall configuration in Control Panel) to enable all traffic from the Raspberry Pi IP address to the specific interface I used in my Windows 7 machine. The link above also explains how to manually configure Windows Firewall from Windows command line.
Hopefully this helps ASP .NET MVC 4 folks out there who play with Raspberry Pi.
- The httplib python module exists in both python 2.7.x and 3.x
- If you want to run http server in Raspberry Pi with python you could use both python 2.7 and 3.2. Just use the SimpleHttpServer module or invoke it with "python -m SimpleHttpServer [port number to listen to]"
- Last but not least, I have changed my Raspberry Pi IP to static IP before conducting this experiment.
Monday, December 17, 2012
Cross Compiling to Raspberry Pi from Windows 7
In this post I will explain how to cross compile a "Hello World!" application from Windows 7 to Raspberry Pi. There's a catch though, I run the cross compiler in Linux Slackware 12 (x86) running inside virtual machine in Windows 7 host :P.
So, first up is prepare the Slackware 12 virtual machine in Windows 7. I used Vmware, but you could use VirtualBox as well. Once you get that running, you can now start preparing for the cross compilation. Download the cross toolchain from: https://github.com/raspberrypi/tools, then decompress it with unzip tool in the shell as follows:
pinczakko@sharingan:~/unzip sources/cross-tools-master.zip -d raspberry_pi_cross_toolswith the command above, the cross-toolchain is now at
~/raspberry_pi_cross_toolsNow, I need to export the path of the cross compilers to my local environment. The path of the cross compilers binaries is at
~/raspberry_pi_cross_tools/arm-bcm2708/gcc-linaro-arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian/binat this point. To add the cross compilers to the environment, I edited
~/.profileand
~/.bashrcto include the following line in the end of both files:
export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/raspberry_pi_cross_tools/arm-bcm2708/gcc-linaro-arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian/binAfter both of the files edited, you have to log out and the log in again to make the environment changes recognized (actually, changing only .profile suffice for our purposes in Slackware 12). Now, once you log in again, you can test whether the environment changes are in effect by invoking one of the compilers. For example:
pinczakko@sharingan:~$ arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc -v Using built-in specs. COLLECT_GCC=arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/home/pinczakko/raspberry_pi_cross_tools/arm-bcm2708/gcc-linaro-arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian/bin/../libexec/gcc/arm-linux-gnueabihf/4.7.2/lto-wrapper Target: arm-linux-gnueabihf Configured with: /cbuild/slaves/oort61/crosstool-ng/builds/arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-linux/.build/src/gcc-linaro-4.7-2012.08/configure --build=i686-build_pc-linux-gnu --host=i686-build_pc-linux-gnu --target=arm-linux-gnueabihf --prefix=/cbuild/slaves/oort61/crosstool-ng/builds/arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-linux/install --with-sysroot=/cbuild/slaves/oort61/crosstool-ng/builds/arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-linux/install/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libc --enable-languages=c,c++,fortran --disable-multilib --with-arch=armv6 --with-tune=arm1176jz-s --with-fpu=vfp --with-float=hard --with-pkgversion='crosstool-NG linaro-1.13.1+bzr2458 - Linaro GCC 2012.08' --with-bugurl=https://bugs.launchpad.net/gcc-linaro --enable-__cxa_atexit --enable-libmudflap --enable-libgomp --enable-libssp --with-gmp=/cbuild/slaves/oort61/crosstool-ng/builds/arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-linux/.build/arm-linux-gnueabihf/build/static --with-mpfr=/cbuild/slaves/oort61/crosstool-ng/builds/arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-linux/.build/arm-linux-gnueabihf/build/static --with-mpc=/cbuild/slaves/oort61/crosstool-ng/builds/arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-linux/.build/arm-linux-gnueabihf/build/static --with-ppl=/cbuild/slaves/oort61/crosstool-ng/builds/arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-linux/.build/arm-linux-gnueabihf/build/static --with-cloog=/cbuild/slaves/oort61/crosstool-ng/builds/arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-linux/.build/arm-linux-gnueabihf/build/static --with-libelf=/cbuild/slaves/oort61/crosstool-ng/builds/arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-linux/.build/arm-linux-gnueabihf/build/static --with-host-libstdcxx='-L/cbuild/slaves/oort61/crosstool-ng/builds/arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-linux/.build/arm-linux-gnueabihf/build/static/lib -lpwl' --enable-threads=posix --disable-libstdcxx-pch --enable-linker-build-id --enable-plugin --enable-gold --with-local-prefix=/cbuild/slaves/oort61/crosstool-ng/builds/arm-linux-gnueabihf-raspbian-linux/install/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libc --enable-c99 --enable-long-long Thread model: posix gcc version 4.7.2 20120731 (prerelease) (crosstool-NG linaro-1.13.1+bzr2458 - Linaro GCC 2012.08)Now I have the cross compiler added to path in the bash shell. I proceed to compile a very simple hello world C application. This is the source code of that application:
#include < stdio.h >
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
printf("Hello World! [cross gcc]\n");
return 0;
}
Invoke this command to compile this source file (I named the file cross_test.c):
arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc -o cross_test cross_test.cThis creates a binary named cross_test. I transfer the binary to the Raspberry Pi with WinSCP and proceed to run it there. This is the result (in PuTTy).
This should be the first step in cross compiling to Raspberry Pi. I know that there are some Windows cross-compilers for Raspberry Pi out there but I have yet to test them.
Thursday, December 13, 2012
Headless Raspberry Pi with Windows 7
Here's what I did:
- Prepare a >= 2GB sdcard and a cellphone charger with 5V and 700mA-1200mA output. I used my friend's Blackberry cellphone charger at the moment, which outputs 5V and 700mA. After further tests, a Samsung smartphone charger with 4.75V and 550mA output works just fine. Perhaps, that's because I didn't load the USB ports with anything at the moment. The sdcard I used is 8GB (V-Gen).
- Download the debian "wheezy" distro from link at http://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads. I use this version: 2012-10-28-wheezy-raspbian.zip. Once installed, this version shows this in SSH:
pi@raspberrypi ~ $ cat /proc/version Linux version 3.2.27+ (dc4@dc4-arm-01) (gcc version 4.7.2 20120731 (prerelease) (crosstool-NG linaro-1.13.1+bzr2458 - Linaro GCC 2012.08) ) #250 PREEMPT Thu Oct 18 19:03:02 BST 2012
- Decompress the debian "wheezy" image and write it to the sdcard with Win32DiskImager available from http://sourceforge.net/projects/win32diskimager/. Becareful to make sure you used the correct sdcard drive (E:,G:, etc.), because you could delete your valuable data if you happen to use the wrong drive when running Win32DiskImager.
- Run DHCP server in your Windows 7 machine. I use DHCP Server V2.3.5, available for free at http://www.dhcpserver.de/dhcpsrv.htm. I set the IP address range of the DHCP server to 192.168.0.1-6 (subnet mask 255.255.255.248) and set the IP address of my laptop ethernet to 192.168.0.1.It turns out the DHCP server gives the Raspberry Pi the IP address of 192.168.0.2. I could ping the Pi without problems.
- If you could now ping the Raspberry Pi without problems, it's time to move to the next stage. Use an SSH client to SSH to the Pi. I used PuTTy. The default user name is: pi and the default password is: raspberry.
Now, screenshot time.First, cpuinfo:
Second, the debian linux version:
Now, you could make changes to the Raspberry Pi in Windows 7 without problems. The next step would be the cross-compilation and creation of applications. Stay tuned.
So far I have tried compiling some hello world code in C and python directly on the Raspberry Pi without problems. But, for some really serious application development, using the cross-toolchain would be preferred.
Because I mostly work with Raspberry Pi as headless machine, it's quite annoying to have dynamic IP address all the time. I decided to make my Raspberry Pi use static IP. All I have to do is edit /etc/network/interfaces file, change eth0 setting to static like so:
iface eth0 inet static address 192.168.137.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.137.1This hardcodes the Pi's eth0 tp 192.168.137.2. This is how it looks like from Pi's remote console (SSH):
I have also "packaged" my Raspberry Pi in a makeshift enclosure made from bricked Abocom WAP252 access point enclosure to ease working with the Pi. I felt the board is too fragile in my workspace without any sort of enclosure, also because of its size, it's quite hard to hold when you're attaching or disconnecting connectors (USB, eth, HDMI, etc.) from the board. Here's how it looks like:
Tuesday, August 14, 2012
Windows Azure SDK Tools on Windows Server 2008 R2 (x64)
Reading various blogs, books and documentation on Windows Azure development will lead you to the Azure specific tools such as csypack, csencrypt and their friends. However, most of them points to the wrong PATH in your Windows installation as to the location of those Azure specific tools in Azure SDK June 2012. In Azure SDK June 2012 installation on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64, the path of those Azure specific tools is:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SDKs\Windows Azure\.NET SDK\2012-06>instead of the path mostly mentioned in tutorials or books, i.e.
C:\Program Files\Windows Azure\xxx
I hope this helps those who starts developing on Windows Azure and longing to know where the Azure specific tools are located on default Azure SDK installation.
Friday, August 3, 2012
OpenGL Bug in AMD E-350 (Brazos) Driver
Driver Packaging Version : 8.871-110627a-121536C
Provider : ATI Technologies Inc.
2D Driver Version : 8.01.01.1171
2D Driver File Path :/REGISTRY/MACHINE/SYSTEM/ControlSet001/Control/CLASS/{4D36E968-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}/0000
Direct3D Version : 7.14.10.0847
OpenGL Version : 6.14.10.10907
AMD VISION Engine Control Center Version : 2011.0627.1558.26805
with this driver, everything worked as expected and I've just noticed that the OpenGL support now increased to OpenGL 4.1. The previous driver only supports up-to OpenGL 4.0.
Friday, July 27, 2012
Perpanjangan Paket Data Tri (3)
Saturday, July 21, 2012
Kazushige Goto is Now with Intel
Now, he is with Intel http://www.linkedin.com/pub/kazushige-goto/40/230/b61. This shows how serious Intel is about HPC these days. I bet he works on the new Xeon Phi lines of product. It's handy to have man like Goto because of his insights into very low-level execution of HPC routines.
Wednesday, July 11, 2012
XmlDocument Class ImportNode() method
Importing a node creates an XmlNode object owned by the importing document, with Name and NodeType identical to the source node. The new object also has the attributes related to namespaces (Prefix, LocalName, and NamespaceURI).After reading the statement at MSDN above, what you should be aware is the ImportNode() method doesn't place the imported set of node in the target XML document. The method merely import the set of node from the context of the source XML document to the target XML document. What I mean by context here have to do with XML namespace. You cannot just place a "rogue" set of nodes without namespace in the target XML document, you have to give a context to the set of nodes, i.e. valid XML namespace, etc. In most cases this is probably what you want to do:
foreach (XmlNode currentNode in facts.DocumentElement.ChildNodes)
{
node = doc.ImportNode(facts.DocumentElement.ChildNodes.Item(i), true);
doc.DocumentElement.AppendChild(node);
i++;
}
The code above copies every single child element of the root element of the facts XmlDocument object (source) to the doc XmlDocument (destination) root element.
So, next time you deal with the ImportNode() method, remember that what it does is related to the XML document instance context.
Saturday, July 7, 2012
Caching XSD Schemas in Your .NET Application
- Goto the project (JeffFerguson.Gepsio project) and change the "Target Framework" to ".NET Framework 4".
- Add the following code to XbrlSchema.cs file:
using System.Net.Cache; // This line added for caching support
//...
public class XbrlSchema
{
//...
private XmlUrlResolver thisXmlUrlResolver;
//...
internal XbrlSchema(XbrlFragment ContainingXbrlFragment,
string SchemaFilename, string BaseDirectory)
{
thisContainingXbrlFragment = ContainingXbrlFragment;
this.Path = GetFullSchemaPath(SchemaFilename, BaseDirectory);
try
{
var schemaReader = XmlTextReader.Create(this.Path);
thisXmlSchema = XmlSchema.Read(schemaReader, null);
thisXmlSchemaSet = new XmlSchemaSet();
///---- START caching with XmlUrlResolver
thisXmlUrlResolver = new XmlUrlResolver();
thisXmlUrlResolver.CachePolicy = new
RequestCachePolicy(RequestCacheLevel.CacheIfAvailable);
thisXmlSchemaSet.XmlResolver = thisXmlUrlResolver;
///----- END caching with XmlUrlResolver
thisXmlSchemaSet.Add(thisXmlSchema);
thisXmlSchemaSet.Compile();
//...
A side note: the CachePolicy member of the XmlUrlResolver class is not available in .NET Framework version < 4.0 . That's the reason why you have to switch the project to .NET Framework 4.0.
Perhaps, you're not aware of this: the call to XmlSchemaSet.Add() will traverse every linked XSD schemas until all of them are resolved. Now, if the location of the schemas are remote, that incurs very high penalty to the speed of your application and that wastes unnecessary bandwidth. In this case, schema caching comes to the rescue.
Friday, June 22, 2012
Amelia Earhart Last Trip Footnote
I have known for several years that the Netherland/Dutch East Indies Government (now Indonesia) did try to establish aviation "center" in Bandung despite its rather bad location (sorrounded by mountains, Bandung was prehistoric lake long ago).
Wednesday, June 20, 2012
Automotive Night Vision (civilian version of FLIR?)
Now, why would Raytheon is in there? if it's not for FLIR tech, then I'd be surprised. The question is: what kind of FLIR sensor is being used? I think it must've been the long-wave infrared (LWIR) cameras because it doesn't need Cryogenic cooling which is almost impossible in the target vehicle, given the required size and energy requirement.
Another question is will this technology be adopted en-masse? Time will tell. But, to be sure this is a dual use tech.
Tuesday, May 22, 2012
Our Distorted View of The Ancient World
The Antikythera Mechanism (http://www.antikythera-mechanism.gr/) is one of them. The precision of this instrument is a silent proof of the ingenuity of our "ancient" predecessors. Perhaps we shouldn't call whoever invent the machine as "ancient" but rather as advanced predecessors.
Perhaps, reinvention is a feature of any advanced civilization, be it human or not. Maybe, very far in the future when a global catasthrope happens and then reinvention happens let's say to our present day radio technology, human living in that time would call us the ancient as well :-).
Tuesday, April 10, 2012
Using Custom Function Calling Convention in IDA Pro
assignI16toI64a proc near pDstI64= word ptr 4 push bp mov bp, sp mov bx, [bp+pDstI64] mov [bx+I64.mWords.mWord0], ax ; <-- this is one of the parameter mov [bx+I64.mWords.mWord1], 0 mov [bx+I64.mDwords.mDword1], 0 mov ax, bx leave retn 2 assignI16toI64a endp
How do we "inform" IDA Pro about the calling convention? Look at this hint from IDA Pro help.
IDA supports the user-defined calling convention. In this calling convention, the user can explicitly specify the locations of arguments and the return value. For example:Let's put this knowledge to the function above. Go to the "Set Function Type" command (the default is "y" keyboard button). Set the function type as follows:
int __usercall func<ebx>(int x, int y<esi>);denotes a function with 2 arguments: the first argument is passed on the stack and the second argument is passed in the ESI register and the return value is stored in the EBX register.
I64* __usercall assignI16toI64a<ax>(short Src<ax>, I64 *pDstI64)
Now, we have the custom function declaration. Let's see how the "auto commenting" works in the call to this function:
push ax ; pDstI64
xor ax, ax ; Src
call assignI16toI64a
As you can see, the function parameter "auto commenting" works as expected, marking the ax register as one of the parameter (as intended).
Friday, March 2, 2012
Simplifying Complex Expression in Reverse Code Engineering
There are several avenues to deal with the complexity. I found these steps to be useable:
- "Translate" the expressions into propositional variables. Just to make it more readable. For example: the (i < sizeof(MY_DATA)) expression could be "translated" as propositional variable A, and so on.
- Once you have the propositions in place. You now have several options to minimize the present expressions.
- If the number of propositional variable is less than or equal to four, Karnaugh Maps (K-Map) is enough. See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karnaugh_map
- If the number of propositional variable is more than four but less than ten, then Quine-McCluskey algorithm ( http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quine%E2%80%93McCluskey_algorithm ) is attractive because the processing time is "bearable" and could help finding the most simplified form precisely. Unfortunately, due to the exponential run-tim nature of the Quine-McCluskey, any values above ten probably requires unpractical amount of time.
- If the number of propositional variable is equal-to or more than ten, then the most attractive option is the Espresso heuristic (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Espresso_heuristic_logic_minimizer ).
Sunday, January 29, 2012
Opting Out Google Ad Tracking
- Go to Google Dashboard (https://www.google.com/dashboard/)
- Sign in to your account
- Go to Google Ads Preferences Manager (http://www.google.com/ads/preferences/?hl=en)
- Choose opt-out in the services you wished not to be tracked (or all of Google services that you use)
Monday, January 16, 2012
How to Recognize The Documentation That You Wrote Has Gone Too Deply Nested?
One of the way to recognize that you have gone too far "nesting" your documentation section. For example, if you have gone to make section v.w.x.y, that means you're now four levels deep. Four levels are already too deep because human brain are not naturally able to remember something with "nesting-level" more than that.
When your nesting has gone too deep, consider creating a new "chapter" and provide a smooth transition into that new "chapter". That way, people will understand what your're trying to say. Monstrous "chapter" is not good or it's better to say that it's a bad writing habit.
Be aware of it next tome you write documentation
Saturday, January 14, 2012
Intel Atom Finally Arrived in Smartphone (x86 malware finally enters the phone)
Well, as Anand points out: http://www.anandtech.com/show/5365/intels-medfield-atom-z2460-arrive-for-smartphones. Intel Atom smartphone will finally arrive this year.
I'm not that much concerned about its performance but I'm really concerned with the "malware legacy" that the platform has. x86, due to its prevalence has been the playing ground for malware "craftsmen" for years. So, when it enters the smartphone space, surely it's a cause for concern. Android NDK provides the "entry point" to "craft" a host of new malware for the platform.
It seems to be there will be a lot of work for the security guys in that particular platform even before its public release from Intel partners.
Friday, January 13, 2012
Modifying Trac User Privilege into Trac Admin
The basics to modify Trac user privilege into Trac admin is explained in detail here: http://trac.edgewall.org/wiki/TracPermissions.
Why would you want to do that? I found an excuse to do just that because I prefer to make changes to milestones, tickets, etc. via the Trac web interface instead of via command line. Now, let's see what you need to do to change a "normal" user login into a trac admin login. You need to run the trac-admin utility from your trac server akin to this example (change the user name as needed):
me@mymachine:$ trac-adminNow, the your_username user should be promoted into Trac admin and you will see the admin button when you login as that user in your Trac web page.permission add TRAC_ADMIN
That's it.